The research programmes coordinated by Professor Giulianini span from basic understanding of crustacean and fish physiological processes, related to growth and reproduction, to applied genetic characterization of fish and crayfish populations for the management of restocking actions.
Development of innovative autocidal methods to control Procambarus clarkii
 The red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852), is a decapod crustacean originating in the South-eastern United States and it is proved to be an invasive species because “it is an agent of change and threatens native biological diversity” (IUCN 2014). P. clarkii was brought in Europe in the early 70s for aquaculture purposes and nowadays it is the most cosmopolitan crayfish, being found in all continents except Australia and Antarctica (Scalici and Gherardi, 2007).
The red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852), is a decapod crustacean originating in the South-eastern United States and it is proved to be an invasive species because “it is an agent of change and threatens native biological diversity” (IUCN 2014). P. clarkii was brought in Europe in the early 70s for aquaculture purposes and nowadays it is the most cosmopolitan crayfish, being found in all continents except Australia and Antarctica (Scalici and Gherardi, 2007).
Growing efforts are directed towards a better understanding of the biology of P. clarkii in order to set new eradicative methods.
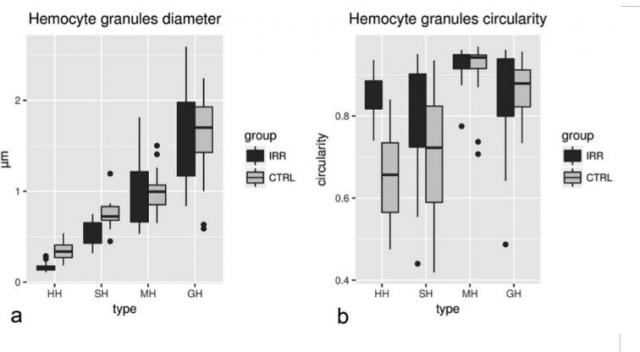 The sterile male release technique (SMRT) has been chosen in Friuli Venezia Giulia region (Italy) as part of the strategy to control the red swamp crayfish local populations. The SMRT consists in the release into the environment of sterile males that are sexually active and able to compete with untreated males for mating partners. Immunocompetence has been chosen to assess the status of health of males after radiation.
The sterile male release technique (SMRT) has been chosen in Friuli Venezia Giulia region (Italy) as part of the strategy to control the red swamp crayfish local populations. The SMRT consists in the release into the environment of sterile males that are sexually active and able to compete with untreated males for mating partners. Immunocompetence has been chosen to assess the status of health of males after radiation.

Circulating haemocytes of males irradiated with a dose of 40 Gy, after 20 days, showed a significantly lower diameter in the granules of hyaline and semigranular haemocytes, but no other evident ultrastructural alterations in comparison with un-irradiated animals were found. Irradiated males showed a significant decrease of about 80% of circulating haemocytes and an increase in frequency of semigranular and granular haemocytes. No significant differences in basal and total phenoloxidase activity were recorded and this could, in part, explain the good survival level of irradiated males despite the drastic decline of the haemocyte number.
We're now focused on finding innovative autocidal methods characterised by the use of species-specific molecules, easy to spread, producible on a large scale and usable all over the year. The D-Phe- Crustacean Hyperglycemic Hormone has been successfully oral-delivered in P. clarkii by using a water/oil/water microemulsion entrapped in a jellified matrix. After the administration of CHH, the glycaemia levels significantly increased in eyestalk-less animals at hour 6, and in intact crayfish at hour 5, from the ingestion.
Genetics of the Salmonidae population for the conservation and management of the native species Salmo marmoratus and Thymallus thymallus in the Friuli Venezia Giulia basins
Ricerca condotta da dr. Silvia Battistella
These species are in decline due to the reduction of habitat and water quality and to competition and / or hybridization with alien ecotypes. Mitochondrial (CR) and nuclear (microsatellite) markers are used for phylogenetic analysis and evaluation of introgression with alien ecotypes.


Grayling, Thymallus thymallus Marble trout, Salmo marmoratus

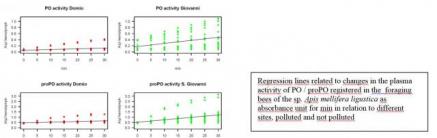
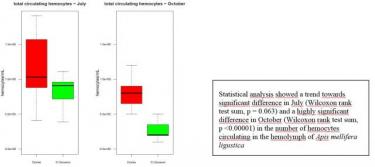
Analysis of some blood parameters in bees, indicators of environmental stress
Ricerca condotta da dr. Silvia Battistella

Analysis of hemolymphatic parameters involved in the humoral immune response (phenol oxidase and its inactive proPO form) and cellular (hemocytes circulating in the hemolymph), used as biomarkers for the detection of pollutants such as pesticides (Eg: Neonicotinoids, systemic insecticides used in maize tanning) in Apis mellifera ligustica.
Ecology of carabid beetles, as bioindicators of environmental quality in relation to the expansion of alien plant species such as Ailanthus altissima in the Gorizia Karst (Northern Adriatic)
Ricerca condotta da dr. Silvia Battistella
The gradient of vegetation, is the first driver of carabid beetles assemblages among plots, with a clear division into species that colonize open habitats (thermophilous and grassland species), semi-open habitats (sylvicolous thermophilous species) and closed habitats (sylvicolous and forest species).
Ailanthus altissima is related to the greater number of species of carabid beetles observed in the study area, in accordance with many other studies that describe a more specific wealth in degraded areas, due to the presence of generalist and opportunistic species. These species show greater mobility and invasive capabilities that allow them to be more abundant in the disturbed habitat, where the availability of prey is higher. If we consider the turnover of the species, A. altissima promotes homogenization of the species.
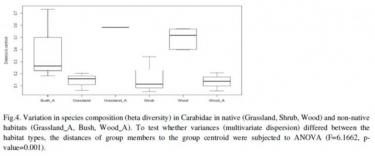
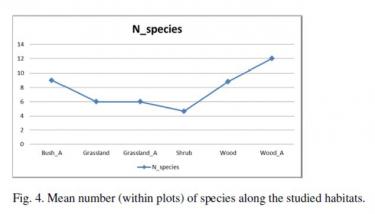
Charts drawn from PhD thesis Dr. Costanza Uboni "THE NEOFITIZATION OF HABITATS AND ITS REPUBLICATION ON VEGETABLE COMPONENTS AND THE FATHERFAUNA OF THE ITALIAN DYNARIC CARSO", of which I was tutor for the animal part.
Ability of DNA barcoding to identify the plant richness and origin presented in the processed honey
Ricerca condotta da dr. Silvia Battistella
Twelve multifloral plus two specific honeys (Santoreggia and Acacia) produced at different sites in a floristically rich area in the North Adriatic Karst were examined by using the ITS2 as barcode markers. An extensive reference database of barcode sequences was generated to determine the taxonomic composition of honey. One hundred and seven plant species were identified in the fourteen honey samples, each of which originated from a mix of common plants belonging to Castanea, Corylus, Quercus, Fagus, Salix and several herbaceous taxa. Interestingly, many typical Karst species were detected in the majority of the honey samples, providing a clear signature for the geographic identity of these products. DNA of the toxic plant Senecio inaequidens was detected in one sample, illustrating the usefulness of DNA barcoding for evaluating the safety of honey, as already reported by Bruni et al. (2015) for the toxic plant Atropa belladonna. More, we detected also the presence of Zygosaccaromices mellis and Malassezia restricta.